Figures for:
Management of Abnormal Cervical/Vaginal Pap Smears
[Medscape General Medicine 1(1), 1999. © 1999 Medscape]
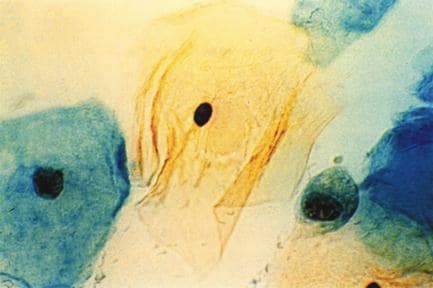
Figure 1. A normal Pap smear.
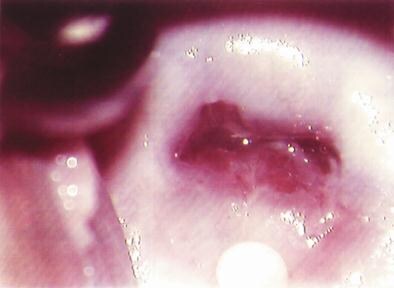
Figure 2. Colposcopic photograph of a normal cervix showing the
squamocolumnar junction with metaplastic changes.
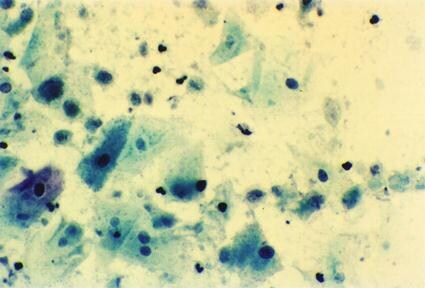
Figure 3. Pap smear showing Trichomonas vaginalis infection
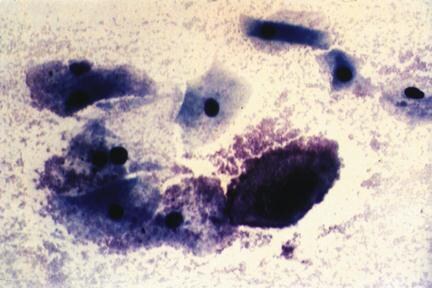
Figure 4. Pap smear showing clue cells consistent with bacterial
vaginosis.
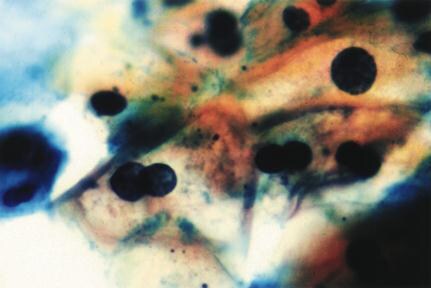
Figure 5. Pap smear showing koilocytes (low-grade squamous intraepithelial
lesion).

Figure 6. Pap smear showing Actinomyces.
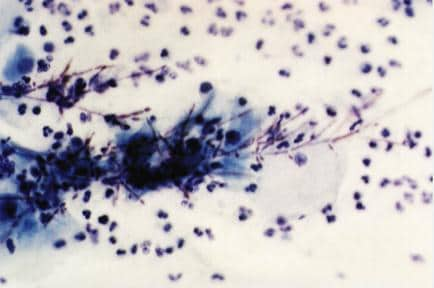
Figure 7. Pap smear showing Candida.
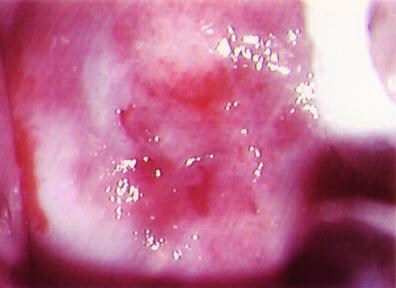
Figure 8. Colposcopic photograph of a cervix showing metaplastic and
inflammatory changes.
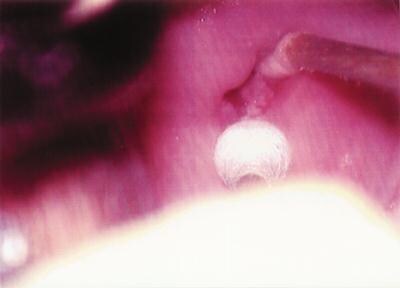
Figure 9. Colposcopic photograph of a cervix showing an acetowhite,
glandular canal lesion (adenocarcinoma-in-situ).
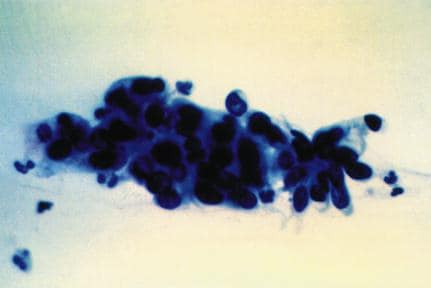
Figure 10. Pap smear showing a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
(severe dysplasia)
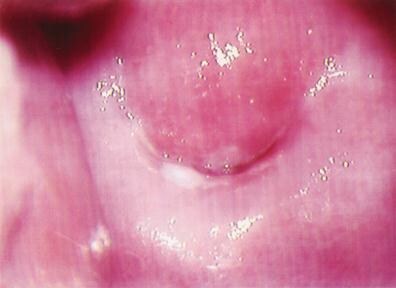
Figure 11. Colposcopic photograph of a cervix showing an acetowhite lesion
on the ectocervix (CIN 2)
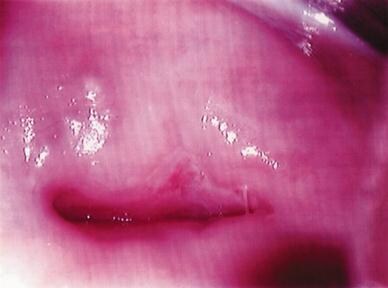
Figure 12. Colposcopic photograph of a cervix showing an acetowhite area
with punctation at the squamocolumnar junction (microinvasion)











